Biodiversity
Initiatives for Biodiversity Conservation
The SHI Group believes that economic and social prosperity is impossible without natural capital, and in accordance with the Sumitomo Heavy Industries Group Environmental Policy, we are promoting initiatives to conserve biodiversity as part of our environmental management efforts, including preventing environmental pollution, and our response to climate change.
Based on the TNFD*1 recommendations, we report the results of our analysis of our Group's dependence on and impact on biodiversity and natural capital.
*1 TNFD (Taskforce on Nature-related Financial Disclosures) is a framework that enables companies and organizations to assess and disclose the impacts of their economic activities on the natural environment and biodiversity.
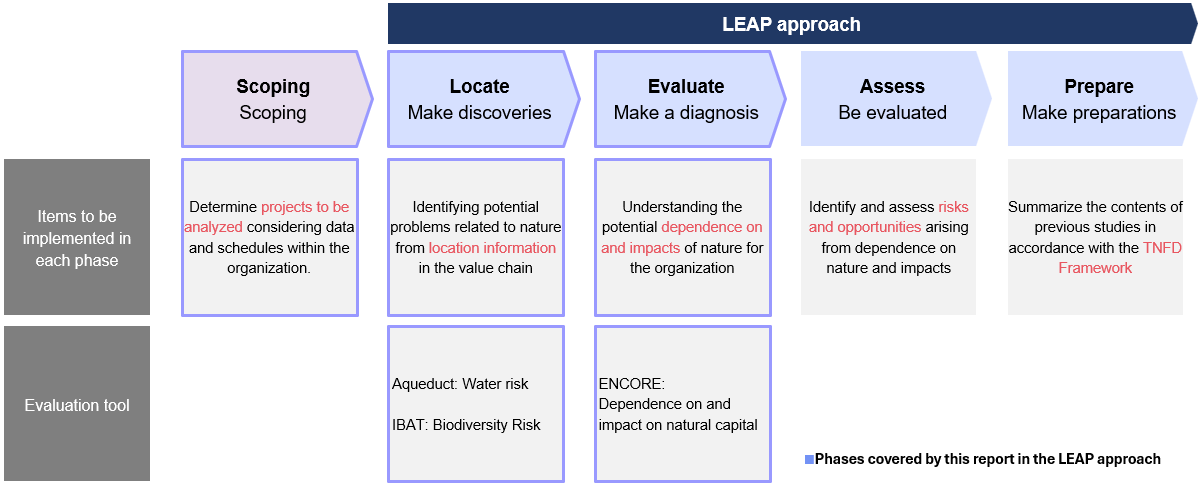
*2 The LEAP approach—Locate, Evaluate, Assess, Prepare—is a process-based guidance designed to help organizations integrate nature-related considerations into their risk management and disclosure practices.
Understanding Our Relationship with Nature Using ENCORE
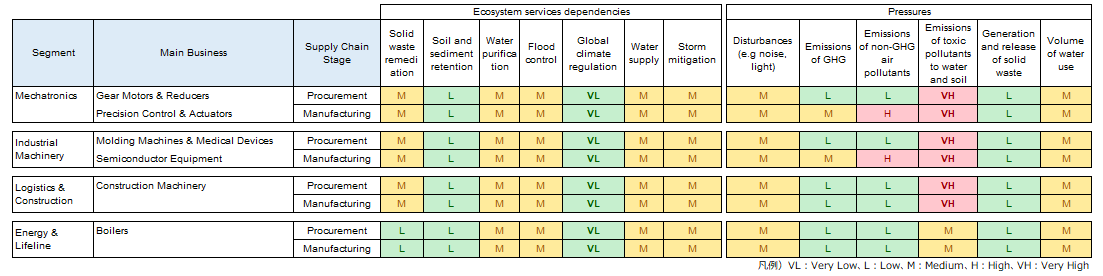
We used “ENCORE※3”, an analysis tool, to analyze the relationship between our main businesses and nature.
Each of the four business segments was selected to analyze the processes related to the main raw materials in procurement (upstream), the business processes in manufacturing (direct operation), and the multiple processes that are considered to have a significant impact on the manufacturing process.
※3 ENCORE, which stands for "Exploring Natural Capital Opportunities, Risks and Exposure," is a free online tool for assessing dependencies and impacts on biodiversity and ecosystem services, helping companies and financial institutions understand nature-related risks.
| Segment | Main Business | Production Process (ENCORE Classification) | Supply Chain Stage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mechatronics | Gear Motors & Reducers | 2591 Forging, pressing, stamping and rolling forming of metals and powder metallurgy | Procurement |
| 2710 Manufacture of electric motors, generators, transformers and electricity distribution and control apparatus | Manufacturing | ||
| 2592 Metal processing, painting and machining | |||
| Precision control・Actuator | 2591 Forging, pressing, stamping and rolling forming of metals and powder metallurgy | Procurement | |
| 2651 Manufacture of measuring, testing, maneuvering and control equipment | Manufacturing | ||
| IM | Molding Machine | 2591 Forging, pressing, stamping and rolling forming of metals and powder metallurgy | Procurement |
| 2829 Manufacture of special-purpose machinery | Manufacturing | ||
| 2592 Metal processing, painting and machining | |||
| Semiconductor equipment | 2591 Manufacture of other fabricated metal products; metalworking service activities | Procurement | |
| 2660 Manufacture of irradiation, electromedical and electrotherapeutic equipment | Manufacturing | ||
| 2610 Manufacture of electronic components and boards | |||
| 2829 Miscellaneous special industrial machinery manufacturing | |||
| Medical devices | 2591 Forging, pressing, stamping and rolling forming of metals and powder metallurgy | Procurement | |
| 2660 Manufacture of irradiation, electromedical and electrotherapeutic equipment | Manufacturing | ||
| L&C | Construction Machinery | 2591 Forging, pressing, stamping and rolling forming of metals and powder metallurgy | Procurement |
| 2824 Machinery manufacturing for molybdenum, quarrying and construction | Manufacturing | ||
| 2592 Metal processing, painting and machining | |||
| E&L | Boiler | 251 Manufacture of structural metal products, tanks, reservoirs and steam generators | Procurement |
| 2513 Steam generators | Manufacturing |
ENCORE analysis results
Our core businesses have found that they are not too dependent on nature.
On the other hand, the impact on nature was Very high for “toxic soil and water pollutants”and high for “non-GHG air pollutants”.
Based on these results, we decided to conduct a separate analysis of water risks.
Risk analysis using Aqueduct
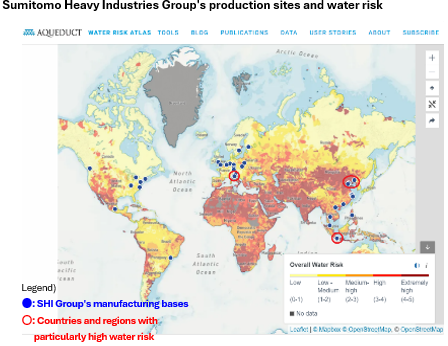
Water risk assessments were conducted at 57 domestic and overseas production sites using the "Aqueduct※4" provided by “WORLD RESOURCES INSTITUTE”.
※4 Aqueduct is a water risk assessment tool provided by the World Resources Institute (WRI) that can map risks such as floods, droughts, and water shortages, and is a data platform that enables companies and governments to identify, understand, and address water risks.
Water risks
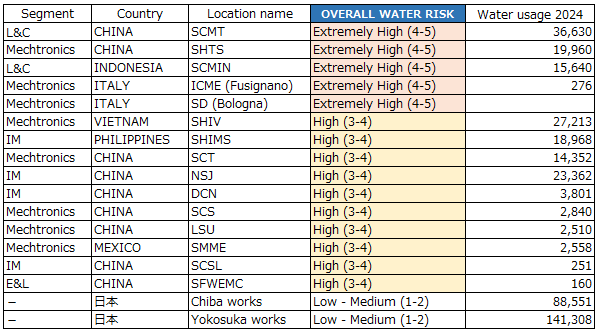
“Overall water risk” resulted in "Extremely High" at five manufacturing sites. We conducted an individual survey of seven sites, including these five sites and two sites in Japan that consume large amounts of water.
Water consumption by the seven targeted sites in FY2024 was 20% of the total for the entire Group.
What is water risk assessment by Aqueduct
| Physical risk: | Risks related to water supply and availability - Evaluation items are "Water stress (total water demand)," "Flood risk (rivers)," and "Flood risk (coastal areas)." |
|---|---|
| Physical risk (quality): | Risks related to water quality - Evaluation items are "untreated wastewater" and "eutrophication" |
| Regulatory Risks: | The potential for changes in water laws and policies to affect business and local water use |
| Reputation risk: | the potential for corporate water use and management to affect social reputation and brand image - Evaluation items are "drinking water" and "sanitation (toilet)" |
Water risk assessment results for each site
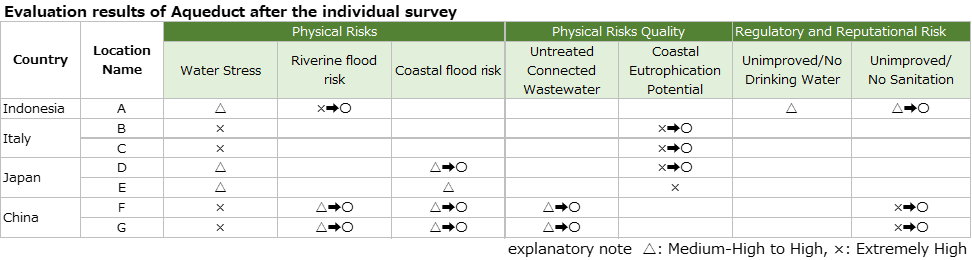
The results of water risk assessments at seven sites are shown in the table below.
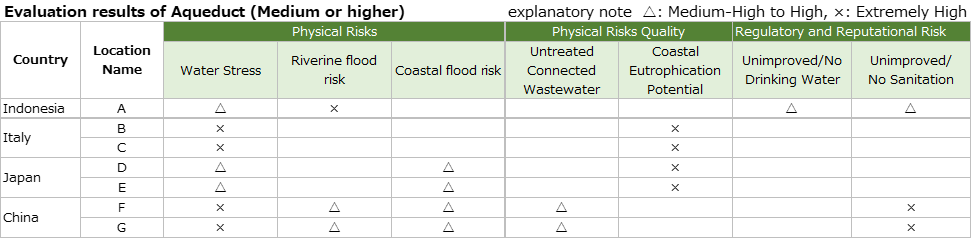
Individual Survey Results on Water Risks
Water Stress
・We surveyed on base A in Indonesia.
This base area faces major challenges, including water pollution caused by industrialization and the difficulty of securing water for daily use due to a lack of infrastructure. Indonesia as a whole is also in an urgent need for sustainable water management due to climate change and deforestation. However, this base has not experienced any water withdrawal restrictions due to drought in recent years. Measures to reduce water usage include the use of water-saving stickers, repairs to underground pipes, and the replacement of aging pipes.
・We surveyed on base B and base C in Italy.
The local government announced a "Drought Emergency Decree" in 2023, and is promoting measures such as accelerating the development of water treatment infrastructure, increasing reservoir capacity, reusing agricultural wastewater, promoting the construction of desalination facilities, and reducing the waste of water resources. Neither base has experienced any water withdrawal restrictions due to drought in recent years, and water usage is limited to employee services.
・We surveyed on base D and base E in Japan.
Chiba City: There are currently no concerns about drought, but there are concerns about the deterioration of water quality due to urbanization and land subsidence due to groundwater use.
Yokosuka City: There are currently no concerns about drought, but there are concerns about the conservation of water sources in the future.
Neither base are heavy water users, but there have been no water withdrawal restrictions due to drought in recent years.
・We surveyed on base F and base G in China.
The areas where both bases are located have extremely scarce water resources, even by the standards of the whole of China, and after the major earthquake in 1976, the water supply system was damaged, resulting in serious water shortages. For this reason, the city has formulated comprehensive water conservation action plans and implemented measures such as reusing dredged mine water in industry (with an 80% reuse rate) and utilising reclaimed water in the city centre (at 60.08%). Neither base has experienced water withdrawal restrictions due to drought in recent years. Reduction measures include modifying dry paint booths and installing water meters to detect leaks early on.
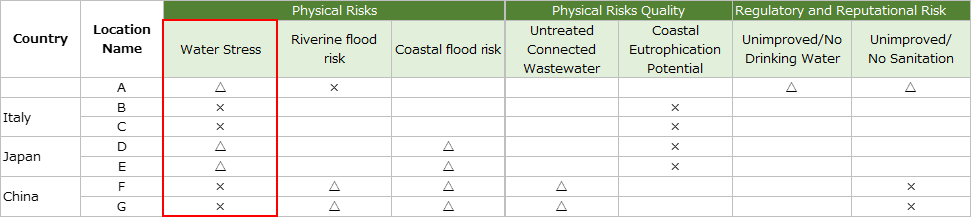
Physical risks (quantities); Flood risks (rivers)
・We surveyed on base A in Indonesia.
The Citarum River, which is a risk basin for Aqueduct, is located approximately 9 km away from the base in a straight line, but the difference in elevation between the base and the river is 80 to 100 m.As one of the flood countermeasures, this base is located in an industrial area where an artificial lake is constructed to accommodate drainage systems and rainwater during heavy rainfall. Therefore, the risk of flooding in this base is small.
・We surveyed on base F and base G in China.
The Ziya River, which is a risk basin of Aqueduct, is located about 9 km in a straight line from both bases, and the difference in elevation from the river is about 6 m, which is small and almost flat. There is no hazard map issued by the Chinese government for both bases areas, but there have been no floods since the establishment of the plant in 2007.
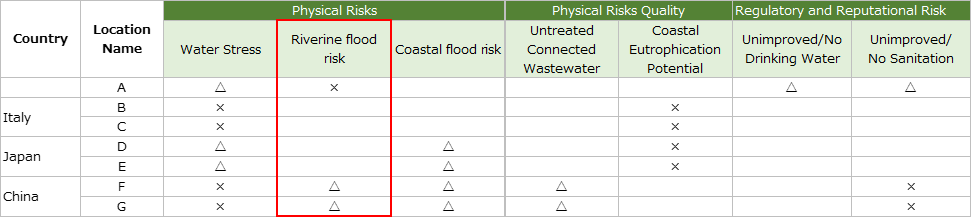
Physical risks (quantities); Flood risks (rivers)
・We surveyed on base D and E in Japan.
Base D is located at a straight distance of 8.5 km and 26 m above sea level. As the storm and flood hazard map of Chiba City is not an inundation risk area, the risk of flooding at the site is small.
・Base E is located 2.3 to 2.6 m above sea level in the coastal area, and the base is 0.3 to 3 m in the high-tide inundation risk area in Kanagawa Prefecture. There were breakwaters along the north-south coast of the premises, and some of the entrances to the buildings had water stoppers. We regularly conduct emergency drills assuming a tsunami, and we were prepared to deal with the risks.
・We surveyed on base F and base G in China.
Both bases are located at an altitude of 24 meters above sea level, and Tanjin Xingang, a risk port in Aqueduct, is a straight-line distance away.
It is located about 100 km away.There is no hazard map issued by the Chinese government for both base areas, but there have been no floods since the plant was established in 2007, so the risk is small.
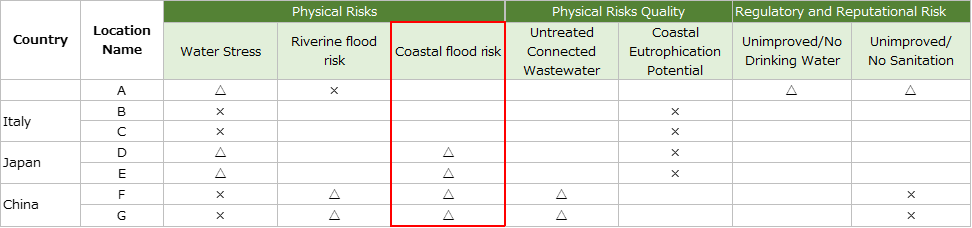
Physical risk (quality); untreated wastewater
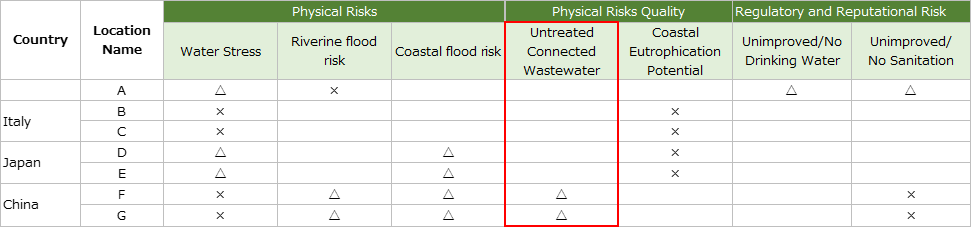
・We surveyed on base F and base G in China.
Process wastewater from base F is a cutting fluid and cleaning agent generated in the machining process. As these are delivered to qualified industrial waste disposal contractors as hazardous waste, they are not discharged from the site without treatment, and the risk is small.
・Process wastewater from base G is treated at the wastewater treatment facility and discharged to the industrial park's industrial drainage network.
Thereafter, it is reprocessed at the city's sewage treatment plant through the network.Therefore, it is unlikely that it will be discharged from the site without treatment, and the risk is small.
Physical risk (quality); eutrophication
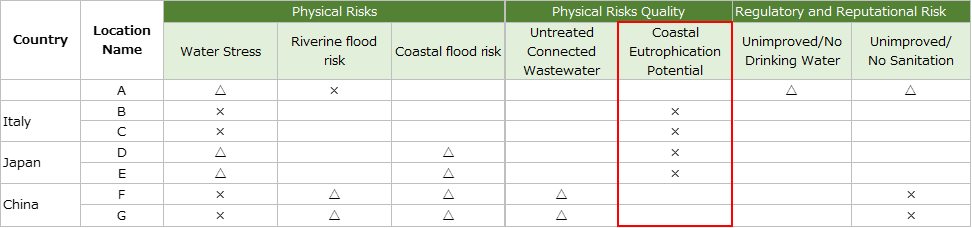
・We surveyed on base B and base C in Italy.
Although there were no water treatment facilities at both sites, there was no wastewater from the process and only domestic wastewater was discharged to sewage.
Therefore, the risk of eutrophication is low.
・We surveyed on base D and base E in Japan.
Base D does not have a water treatment facility, but it was discharged into the sewage system.
Therefore, the risk of eutrophication is low.
・Base E is discharged into the ocean via a water treatment facility. However, Tokyo Bay, where the discharge is made, is subject to total emission control. Therefore, automatic measurement was conducted to monitor the discharge in accordance with the effluent standard*.
Therefore, it can be said that we are prepared to cope with the risk of eutrophication.
*:Effluent standards based on the Water Pollution Control Law and the Kanagawa Prefecture Ordinance for Conservation of the Living Environment
Regulatory and reputation risks; drinking-water
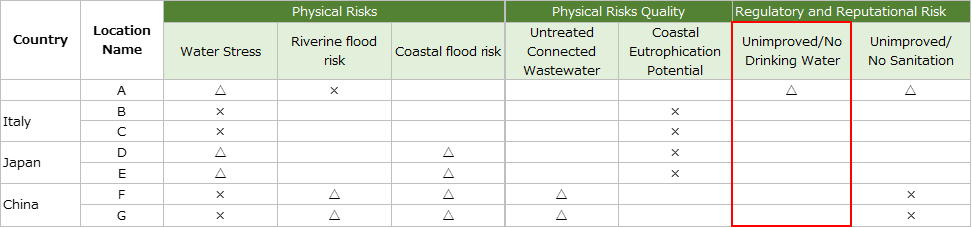
・We surveyed on base A in Indonesia.
This base provides mineral water for drinking needs. In addition to gallon containers for dispensers, PET bottles are available for meetings and guests.
Water for production (painting) and sanitation purposes is supplied from the industrial park and stored on the ground tank.
Bottled mineral water for drinking water and water supplied from industrial parks are analyzed to ensure that they are within safe and usable quality thresholds. Therefore, it can be said that preparations are being made to cope with drinking water risks.
Regulatory and reputational risks; sanitary conditions (toilets)
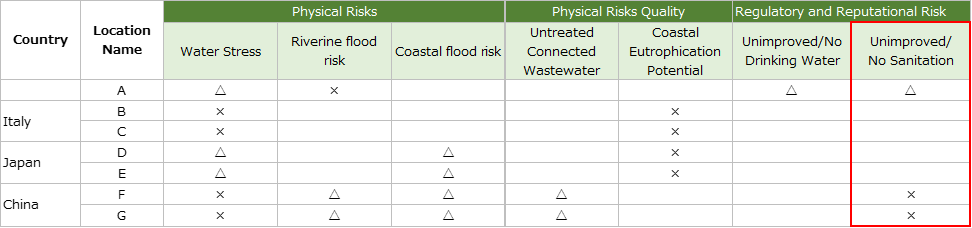
・We surveyed on base F and base G in China.
Both bases used tap water, and the toilets used were washed. Wastewater is discharged into the sewage via the septic tank, so sanitary conditions are good.
・We surveyed on base A in Indonesia.
This base used water supplied by the industrial park, and the toilet was flushed. Wastewater is treated from a closed drainage system via sedimentation tanks at the Wastewater Treatment Plant (WWTP) in the industrial park, so it can be said that the sanitary conditions are good.
Summary of Individual Survey Results and Future plans
Summary of Individual Survey Results
Based on the results of interviews and on-site surveys of seven targeted bases, it was found that water risks were low at all sites, or that water risks were prepared and operated.
The following table shows the evaluation results of Aqueduct after the individual survey.
Future plans
We will also continue to conduct individual surveys at sites with “Overall water risk” and “High” or below to identify water risks at all production sites.
Endorsement of Keidanren Initiative for Biodiversity Conservation
In pursuit of a sustainable society, SHI Group has endorsed the Keidanren Initiative for Biodiversity Conservation, which outlines corporate intent and action guidelines for addressing biodiversity-related challenges.
Our key activities under this initiative include reducing wood usage in packaging, tackling the issue of marine plastics, and promoting green spaces and tree planting around our production facilities.
