 |
|
|
 Rolling Rolling |
| Shaping
and deforming materials by passing them through two and more revolving rolls. Depending
on the treating temperature, Classification is made into hot rolling and cold
rolling. |
|
 Adamite
Roll Adamite
Roll |
|
Semi-steel base rolls having a high friction coefficient.
A higher friction coefficient improves biting rolled materials. The special
treatment applied can enhance their properties of anti-fire cracking and
toughness. Adamite rolls are applied to billeting mills and rough trains of bar
mills.
|
|
 Rolling
mill rolls Rolling
mill rolls |
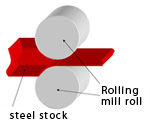 |
Rolls employed in blast furnace steel
manufacturers and electric furnace steel manufacturers for rolling (the
functions of which are pressing and extending by revolving rolls) steel stock
like slabs and bars. Mechanical properties of steel rolled are drastically
improved. |
|
|
|
|
 Mold Mold |
| A container that is used to give its shape to molten metal that is poured.
The molds are classified into sand mold, cement mold, metal mold, etc. |
|
 Spin Casting (Centrifugal Casting) Spin Casting (Centrifugal Casting) |
| A casting method to pour molten metal into a high speed revolving mold.
The method is classified into vertical method, horizontal method, and inclined
method ( as an intermediate method). |
|
 SIP Roll SIP Roll |
Rolls given our original heat treatment performed. SIP comes from “Sumitomo
Improved Penetration.” The finer microstructure in the subsurface zone
and their lower mass effect are realized along with breakage resistance,
anti-surface deterioration and anti-fire cracking improved.
>>Details |
|
 Grain Roll (Indefinite Chilled Iron Roll) Grain Roll (Indefinite Chilled Iron Roll) |
Roll material with one of long history. With flaky graphite and cementite
in its microstructure, grain rolls of a high hardness are superior not
only in wear resistance but also in anti-fire cracking, and are usually
applied to the finishing stand of the hot strip mills and pipe rolling
mills.
>>Details |
|
|
|
 Graphitic Steel Roll Graphitic Steel Roll |
Semi-steel rolls with small spherical-like graphite precipitated in the
microscopic structure usually applied in order to improve Adamite rolls’
inferior properties of anti-fire cracking and anti-burned sticking.
>>Details |
|
 Adjustable Inclined Centrifugal Casting Machine for small size Adjustable Inclined Centrifugal Casting Machine for small size |
Shell melt is poured into the high speed revolving mold at a low inclination
angle setting, and then core melt is poured step by step into the reduced
speed revolving mold at step-by-step further inclination angle settings.
Productivity is improved in comparison with its counterpart (the vertical
method and the horizontal method). The fine microstructure free from the
microscopic dendritic growth generated by vertical method enhances resistance
to fire cracks and surface deterioration. The shell can be produced to
be thicker than the vertical method.
>>Details |
|
 Core Material Core Material |
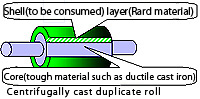 |
The central cylindrical part of a duplicate roll (the outer part
of a roll barrel is called shell.) The duplicate rolls are conventionally
produced by the centrifugal casting method. The core and the shell are
metallurgically bonded. |
|
|
 Static Casting Static Casting |
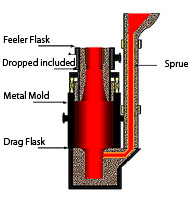 |
The most common way to pour molten metal into the molds which sit usually
on the bed of a pit. The rolls with a hardness of approximately less than
HSC 70 are cast this way.
>>Details |
|
|
|
|
 Ductile Iron Rolls (Spheroidal Graphite Cast Iron Rolls) Ductile Iron Rolls (Spheroidal Graphite Cast Iron Rolls) |
Spheroidal graphite cast iron rolls with spheroidal graphite precipitated
in the matrix of the microscopic structure, excellent in strength and anti-fire
cracking. The applications of ductile iron rolls are extensive, ranging
from slabbing & blooming rolls to finishing train rolls of the wire
rod mills.
>>Details |
|
 Iron Base Rolls Iron Base Rolls |
The iron base rolls are divided into grain (indefinite chilled cast iron)
roll, ductile (spheroidal graphite cast) iron roll and definite chilled
cast iron roll. The grain rolls have some flaky graphite in the matrix
of the microscopic structure, the ductile iron rolls some spheroidal graphite,
and the definite chilled cast iron rolls no graphite.
>>Details |
|
|
|
 Hot Rolling Hot Rolling |
| Rolling performed above the recrystallization temperature of rolled metal
stock. |
|
 High Speed Tool Steel Base Rolls (Sumitomo material code “STZ”) High Speed Tool Steel Base Rolls (Sumitomo material code “STZ”) |
Rolls with intermediate properties between ductile iron rolls and rolls
of semi-steel base like adamite and ordinary high speed tool steel base
rolls. The rolls possess conflicting properties of high resistance to heat
cracking, surface deterioration and high toughness as well as high resistance
to wear.
>>Details |
|
 Steel Base(Semi-steel Base) Rolls Steel Base(Semi-steel Base) Rolls |
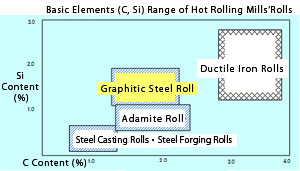 |
Steel Base(Semi-steel Base) Rolls are classified into Adamite rolls and
graphitic steel rolls. The rolls show a low hardness drop from groove surface
to the cross sectional center and possess a high friction coefficient good
for biting. Good biting is usually required for rolls for slabbing &
blooming mills, billeting mills and the rough train of bar mills, for which
anti-heat cracking properties and high toughness are also required. Steel
base (semi-steel base) rolls applied to the rolled for mills mentioned
above. |
|
|
 Centrifugal Casting Composite Rolls Centrifugal Casting Composite Rolls |
 |
Rolls manufactured making use of centrifugal force generated by revolving
a mold. A hard material with a high wear resistance is poured for the shell
of roll barrel, and a soft and tough material with a high resistance to
breakage is poured for the core of roll. The interface between the shell
and the core is metallurgically bonded The core is usually of ductile cast
iron with a high strength.
|
|
|
|
|
 Cold Rolling Cold Rolling |
| Rolling performed under the recrystallization temperature of rolled metal
stock. |
|
 High Speed Tool Steel Base Rolls High Speed Tool Steel Base Rolls |
| Rolls with a higher content of carbon and hard particle forming alloy elements
compared with those of tools of high speed tool steel to improve drastically
resistance to wear and surface deterioration by precipitation of hard carbides
of MC, M2C and M7C3 in the microscopic structure. |
|
 |
|



